Renal Cell Carcinoma
Comprehensive treatment for kidney cancer, including surgery, immunotherapy, and targeted therapy.
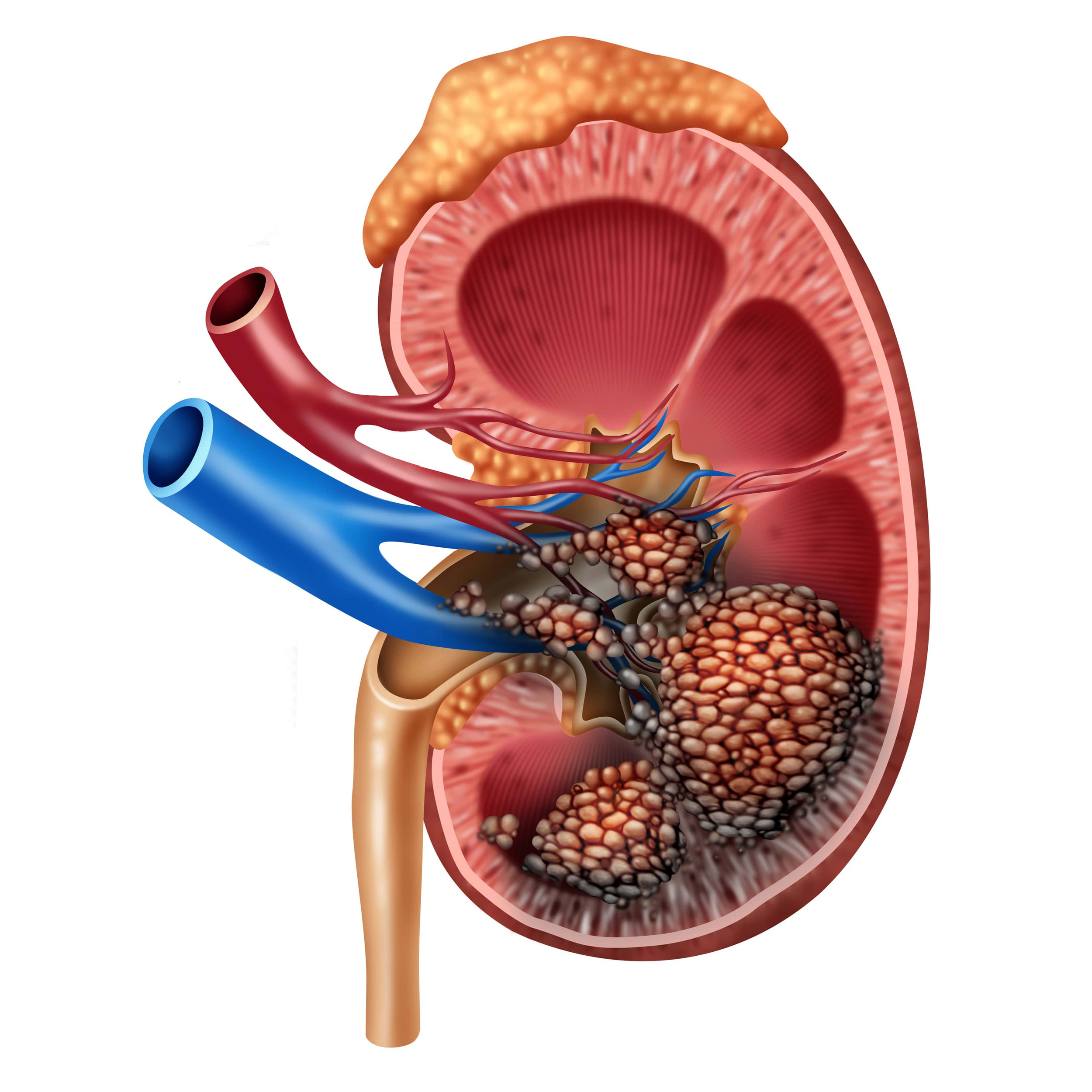
Renal Cell Carcinoma
Solid Tumors
Overview
Renal cell carcinoma is the most common type of kidney cancer. Treatment has advanced significantly with immunotherapy and targeted therapy. Early-stage disease is often curable with surgery, while advanced disease benefits from systemic therapies.
When to Consult
After diagnosis of kidney cancer, detection of kidney mass, blood in urine, flank pain, or unexplained weight loss.
What to Bring
CT/MRI scans, biopsy reports, blood test results including kidney function tests, genetic testing results (VHL, MET), and family history.
Risk Factors
Causes
Treatment Options
Partial Nephrectomy
Removal of tumor while preserving healthy kidney tissue. Preferred when possible to maintain kidney function. Can be done laparoscopically or robotically.
Radical Nephrectomy
Complete removal of affected kidney, surrounding tissue, and sometimes adrenal gland. May be necessary for large tumors or when partial nephrectomy not feasible.
Ablation Therapy
Radiofrequency or cryoablation for small tumors (<4cm) in patients who cannot undergo surgery. Minimally invasive option.
Immunotherapy
Nivolumab plus ipilimumab or pembrolizumab plus axitinib for advanced disease. Immune checkpoint inhibitors showing excellent results. May be used as first-line or second-line treatment.
Targeted Therapy
Sunitinib, pazopanib, axitinib, or cabozantinib (tyrosine kinase inhibitors) blocking VEGF pathway. Temsirolimus or everolimus (mTOR inhibitors). Based on risk stratification and prior treatment.
Adjuvant Therapy
Pembrolizumab after surgery for high-risk localized disease to reduce recurrence risk.
Cytoreductive Nephrectomy
Surgical removal of primary kidney tumor in metastatic disease. May improve outcomes when combined with systemic therapy in selected patients.
Radiation Therapy
Stereotactic body radiation therapy (SBRT) for metastases or primary tumor in patients who cannot have surgery. Palliative radiation for symptom control.
Metastasectomy
Surgical removal of isolated metastases (lung, liver, bone) when feasible. May improve survival in selected cases.
