Ovarian Cysts
Evaluation and management of ovarian cysts, including monitoring and treatment when necessary.
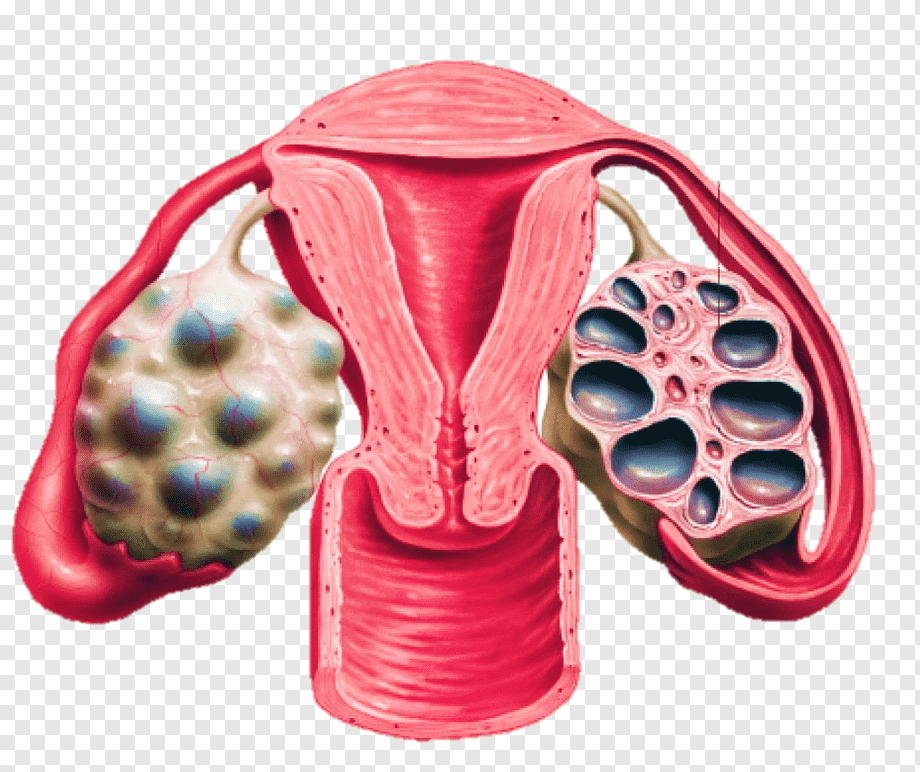
Ovarian Cysts
Solid Tumors
Overview
Most ovarian cysts are benign and resolve spontaneously. However, some may be cancerous or cause symptoms requiring treatment. Careful evaluation distinguishes benign from malignant cysts, guiding appropriate management.
When to Consult
If diagnosed with ovarian cysts, experiencing pelvic pain, bloating, irregular periods, or suspicious imaging findings.
What to Bring
Ultrasound reports, CA-125 blood test results, HE4 test results, genetic testing (BRCA1/2) if available, and complete gynecological history.
Risk Factors
Causes
Treatment Options
Watchful Waiting
Monitoring with regular ultrasounds for simple, small cysts (<5cm) in premenopausal women. Most functional cysts resolve within 2-3 menstrual cycles without treatment.
Hormonal Contraceptives
Birth control pills to prevent new functional cysts and reduce risk of cyst-related complications. Does not shrink existing cysts but prevents formation.
Laparoscopic Cystectomy
Minimally invasive surgical removal of cyst while preserving ovary. Preferred for benign cysts in women wanting to preserve fertility. Small incisions, faster recovery.
Oophorectomy
Removal of affected ovary. May be necessary for large cysts, suspicious features, or postmenopausal women. Bilateral oophorectomy for cancer prevention in high-risk patients.
Laparotomy
Open abdominal surgery for large cysts, suspected cancer, or when laparoscopy not feasible. Allows thorough examination and staging if cancer found.
Aspiration
Draining cyst fluid under ultrasound guidance. Rarely used due to high recurrence rate and risk of missing cancer. Not recommended for suspicious cysts.
Cancer Treatment
If cyst is malignant, treatment includes surgery (debulking), chemotherapy (typically carboplatin/paclitaxel), targeted therapy (PARP inhibitors for BRCA mutations), and possibly radiation.
