Malignant Melanoma
Expert care for melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer, with advanced treatment options.
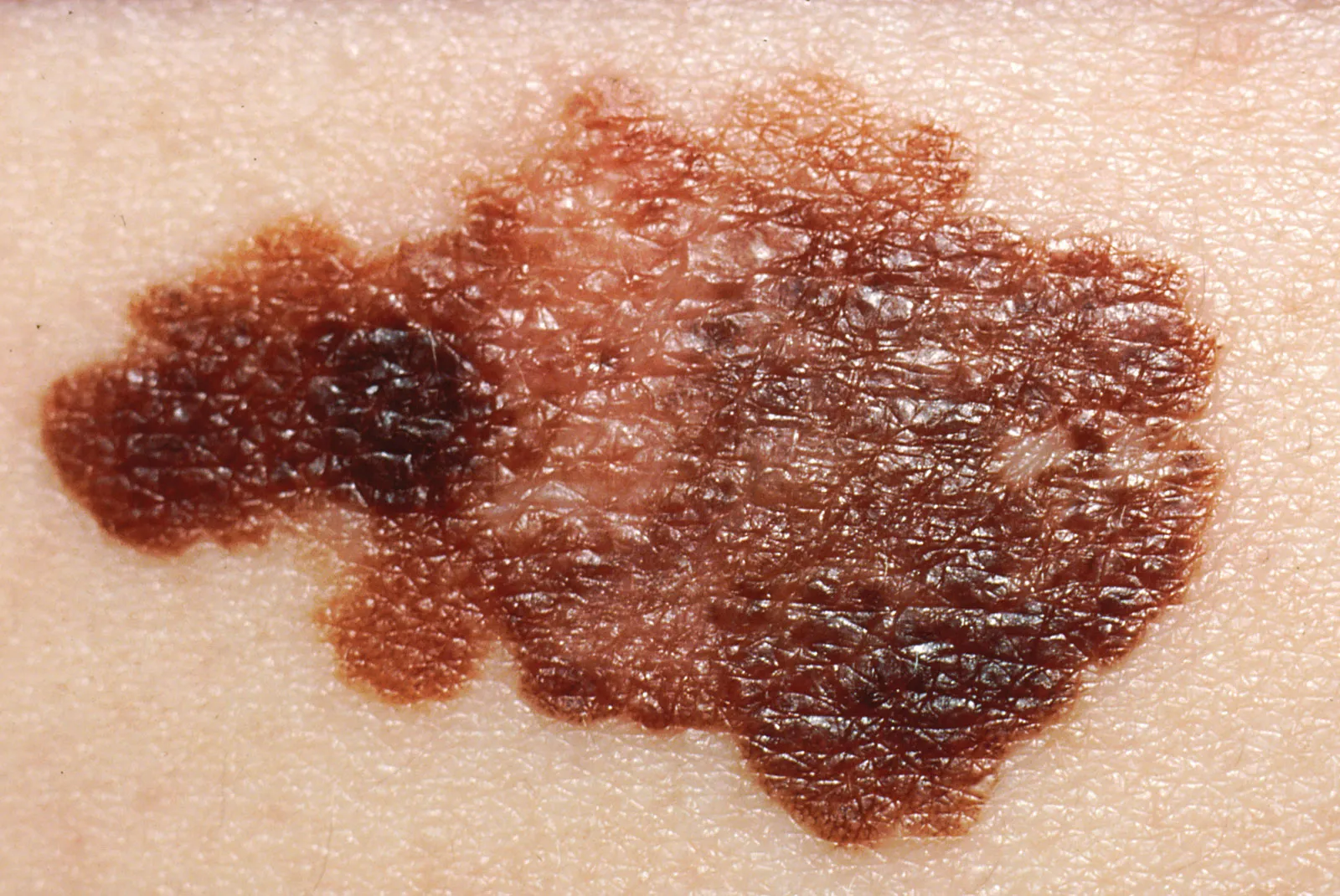
Malignant Melanoma
Solid Tumors
Overview
Melanoma is the most serious skin cancer but highly treatable when caught early. Advanced melanoma has seen remarkable progress with immunotherapy and targeted therapy. Treatment depends on stage, thickness (Breslow depth), ulceration, and molecular characteristics.
When to Consult
If you have a suspicious mole (changing size, shape, color), new pigmented lesion, or confirmed melanoma diagnosis.
What to Bring
Biopsy reports, photographs of the lesion, sentinel lymph node biopsy results, BRAF mutation testing, CT/MRI scans if advanced, and any previous treatment records.
Risk Factors
Causes
Treatment Options
Wide Local Excision
Surgical removal of melanoma with margins based on tumor thickness. Margins typically 1-2cm depending on Breslow depth. Primary treatment for localized melanoma.
Sentinel Lymph Node Biopsy
Removal and examination of first lymph node(s) draining the tumor area. Important for staging and determining need for further treatment.
Lymph Node Dissection
Complete removal of regional lymph nodes if sentinel node is positive. May reduce recurrence risk but can cause lymphedema.
Adjuvant Immunotherapy
Pembrolizumab or nivolumab after surgery for high-risk stage II/III melanoma to reduce recurrence risk. Treatment duration typically 1 year.
BRAF/MEK Targeted Therapy
Dabrafenib/trametinib or vemurafenib/cobimetinib for BRAF-mutated melanoma. Highly effective for advanced disease. May be used as adjuvant therapy or for metastatic disease.
Immunotherapy for Advanced Disease
Nivolumab plus ipilimumab or pembrolizumab alone for metastatic melanoma. Immune checkpoint inhibitors showing remarkable long-term responses. May be first-line or second-line treatment.
T-VEC (Talimogene Laherparepvec)
Oncolytic virus therapy injected directly into melanoma lesions. Stimulates immune response. Used for unresectable stage III/IV melanoma.
Radiation Therapy
External beam radiation for brain metastases, local recurrences, or palliative care. Stereotactic radiosurgery for brain lesions.
Isolated Limb Perfusion
High-dose chemotherapy delivered directly to affected limb for advanced melanoma confined to extremity. Minimizes systemic side effects.
Metastasectomy
Surgical removal of isolated metastases (lung, liver, brain) when feasible. May improve survival in selected cases.
