Malignant Melanoma
Expert care for melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer, with advanced treatment options.
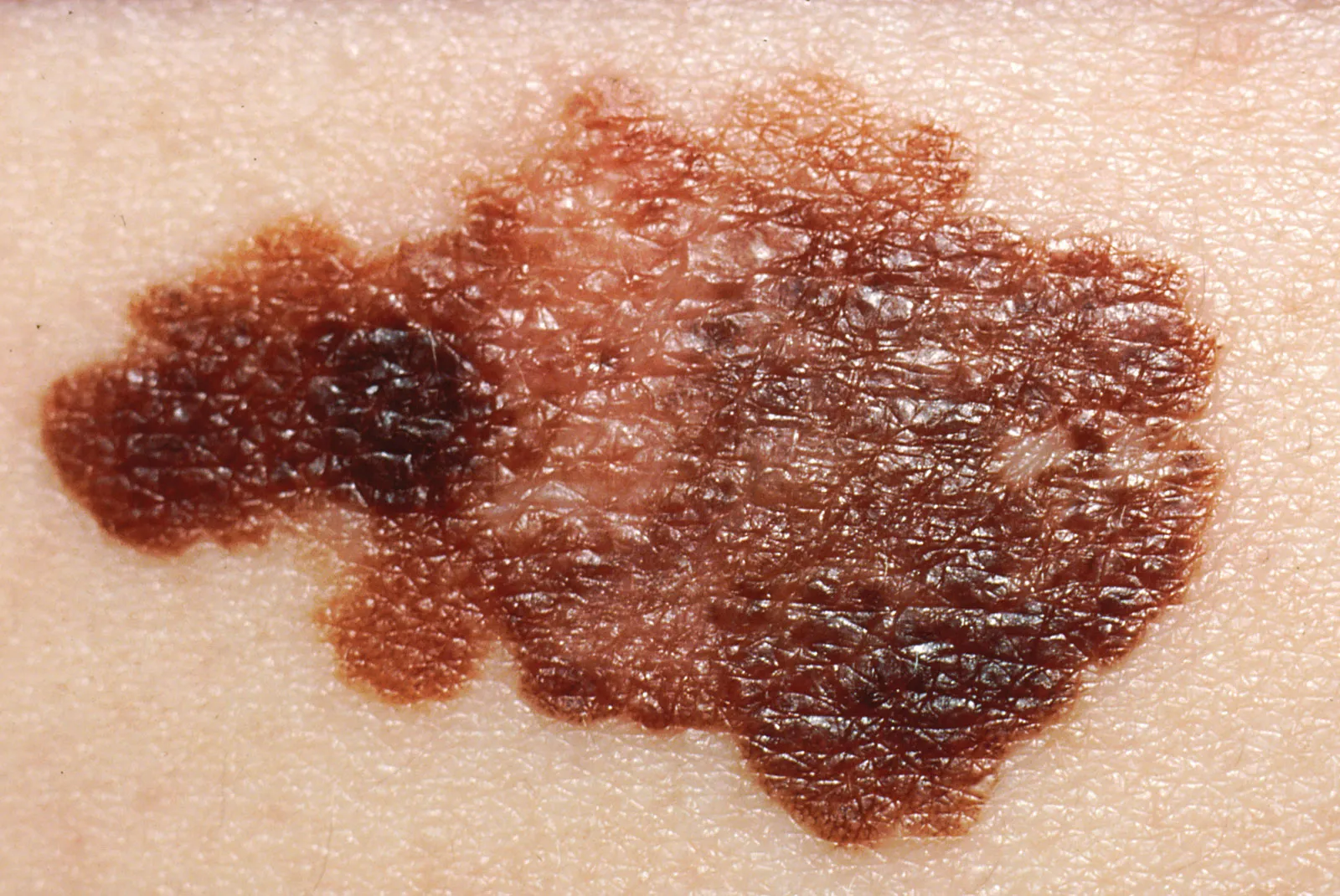
Malignant Melanoma
Solid Tumors
Overview
Expert care for melanoma, the most serious type of skin cancer, with advanced treatment options.
When to Consult
If you have a suspicious mole or confirmed melanoma diagnosis.
What to Bring
Biopsy reports, photographs of the lesion, and any previous treatment records.
Risk Factors
Causes
Treatment Options
Surgical Excision
Wide local excision to remove the melanoma and surrounding healthy tissue. Margin size depends on tumor thickness. Sentinel lymph node biopsy may be performed to check for spread to nearby lymph nodes.
Lymph Node Dissection
Removal of regional lymph nodes if melanoma has spread. Performed when sentinel node biopsy shows cancer cells or when lymph nodes are clinically involved.
Immunotherapy
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ipilimumab, nivolumab, pembrolizumab) that help the immune system recognize and attack melanoma cells. Highly effective for advanced or metastatic melanoma, often used as adjuvant therapy.
Targeted Therapy
BRAF inhibitors (vemurafenib, dabrafenib) and MEK inhibitors (trametinib, cobimetinib) for BRAF-mutated melanomas. Combination targeted therapy offers improved outcomes for patients with specific genetic mutations.
Radiation Therapy
High-energy radiation to destroy remaining cancer cells after surgery, treat lymph node metastases, or for palliative care of brain or bone metastases. Less commonly used as primary treatment.
Chemotherapy
Systemic drug therapy (dacarbazine, temozolomide) for advanced melanoma when immunotherapy or targeted therapy are not suitable. Less commonly used now due to better outcomes with newer treatments.
