Hairy Cell Leukemia
Specialized treatment for hairy cell leukemia, a rare type of chronic leukemia, with effective chemotherapy options.
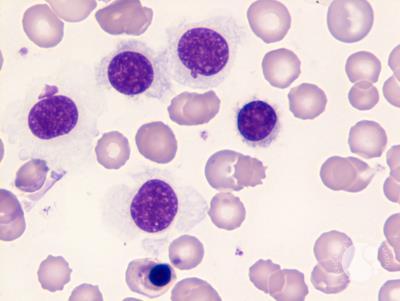
Hairy Cell Leukemia
Hematologic Malignancies
Overview
Hairy cell leukemia is a rare, indolent B-cell leukemia with excellent treatment outcomes. Most patients achieve long-term remission with purine analogs. Treatment is highly effective, and many patients live normal lifespans.
When to Consult
Upon diagnosis of hairy cell leukemia, abnormal blood counts (low platelets, low white cells, anemia), fatigue, infections, or enlarged spleen.
What to Bring
Complete blood count (CBC), peripheral smear, bone marrow biopsy reports, flow cytometry results, BRAF mutation testing, and imaging scans.
Risk Factors
Causes
Treatment Options
Cladribine (2-CdA)
Purine analog chemotherapy, highly effective first-line treatment. Single course often achieves complete remission. Administered intravenously over 5-7 days. High cure rates.
Pentostatin
Alternative purine analog for hairy cell leukemia. Effective first-line option. Given every 2 weeks for several months. Excellent response rates.
Rituximab
Monoclonal antibody targeting CD20 on B-cells. May be used alone or combined with chemotherapy. Effective for relapsed disease or as first-line in selected cases.
BRAF Inhibitors
Vemurafenib or dabrafenib targeting BRAF V600E mutation. Showing promise for relapsed/refractory disease. Targeted approach based on molecular characteristics.
Splenectomy
Surgical removal of enlarged spleen. Rarely needed now with effective chemotherapy, but may be considered for massive splenomegaly or complications.
Interferon Alpha
Historical treatment, rarely used now. May be considered in specific situations or when chemotherapy not suitable.
Supportive Care
Blood transfusions, growth factors, antibiotics for infections, and monitoring for complications during treatment.
